Open and Short Circuit Test of Transformer
Open and short circuit tests are performed on a transformer to determine the:
- Equivalent circuit of transformer
- Voltage regulation of transformer
- Efficiency of transformer
The power required for open circuit tests and short circuit tests on a transformer is equal to the power loss occurring in the transformer.
Open Circuit Test on Transformer
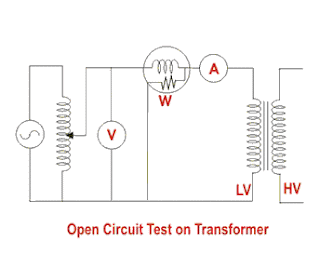
The connection diagram for open circuit test on transformer is shown in the figure. A voltmeter, wattmeter, and an ammeter are connected in LV side of the transformer as shown. The voltage at rated frequency is applied to that LV side with the help of a variac of variable ratio auto transformer.
The HV side of the transformer is kept open. Now with the help of variac, applied voltage gets slowly increased until the voltmeter gives reading equal to the rated voltage of the LV side. After reaching rated LV side voltage, we record all the three instruments reading (Voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter readings).
The ammeter reading gives the no load current Ie. As no load current Ie is quite small compared to rated current of the transformer, the voltage drops due to this current that can be taken as negligible.
Since voltmeter reading V1 can be considered equal to the secondary induced voltage of the transformer, wattmeter reading indicates the input power during the test. As the transformer is open circuited, there is no output, hence the input power here consists of core losses in transformer and copper loss in transformer during no load condition. But as said earlier, the no-load current in the transformer is quite small compared to the full load current so, we can neglect the copper loss due to the no-load current. Hence, can take the wattmeter reading as equal to the core losses in the transformer.
Let us consider wattmeter reading is Po.
If, Zm is shunt branch impedance of transformer.
Therefore, if shunt branch reactance of transformer is Xm,
These values are referred to the LV side of the transformer due to the tests being conducted on the LV side of transformer . These values could easily be referred to HV side by multiplying these values with square of transformation ratio.
Therefore it is seen that the open circuit test on transformer is used to determine core losses in transformer and parameters of the shunt branch of the equivalent circuit of the transformer.
Short Circuit Test on Transformer
The connection diagram for short circuit test on transformer is shown in the figure. A voltmeter, wattmeter, and an ammeter are connected in HV side of the transformer as shown. The voltage at rated frequency is applied to that HV side with the help of a variac of variable ratio auto transformer. We short-circuit the LV side of the transformer. Now with the help of variac applied voltage is slowly increased until the wattmeter, and an ammeter gives reading equal to the rated current of the HV side.
After reaching rated current of HV side, we record all the three instruments reading (Voltmeter, Ammeter and Watt-meter readings). The ammeter reading gives the primary equivalent of full load current IL. As the voltage applied for full load current in short circuit test on transformer is quite small compared to the rated primary voltage of the transformer, the core losses in transformer can be taken as negligible here.
Let’s say, voltmeter reading is Vsc. The watt-meter reading indicates the input power during the test. As we have short-circuited the transformer, there is no output; hence the input power here consists of copper losses in the transformer. Since the applied voltage Vsc is short circuit voltage in the transformer and hence it is quite small compared to the rated voltage, so, we can neglect the core loss due to the small applied voltage. Hence the wattmeter reading can be taken as equal to copper losses in the transformer. Let us consider wattmeter reading is Psc.
If, Ze is equivalent impedance of transformer.
Therefore, if equivalent reactance of transformer is Xe.
These values are referred to the HV side of the transformer as the test is conducted on the HV side of the transformer. These values could easily be converted to the LV side by dividing these values with the square of transformation ratio.
Hence the short-circuit test of a transformer is used to determine copper losses in the transformer at full load. It is also used to obtain the parameters to approximate the equivalent circuit of a transformer .



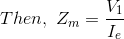










No comments:
Post a Comment